Archives
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-11
- 2018-10
- 2018-07
-
The primary cancer lesion was mostly in
2022-08-04
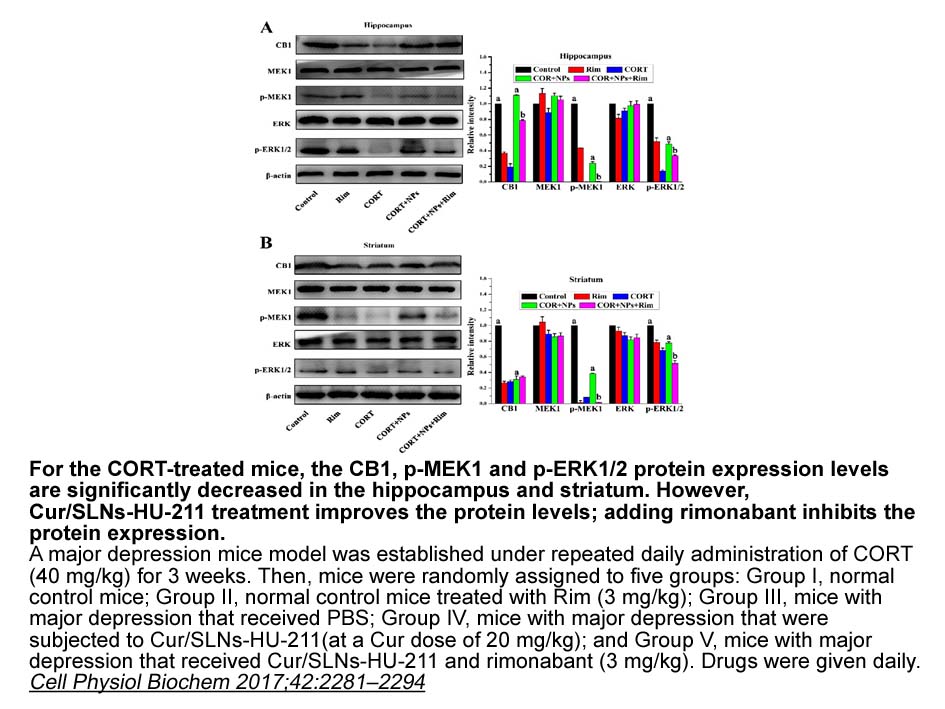
The primary cancer lesion was mostly in the uterus and adnexa, followed by the gastrointestinal tract, brain, blood, and kidney and PX 866 receptor (Fig. 2A). Histopathological findings indicated that most cancers were adenocarcinomas, followed by squamous cell carcinomas, glioblastomas, malignant
-
Depletion of PI P e g by
2022-08-04
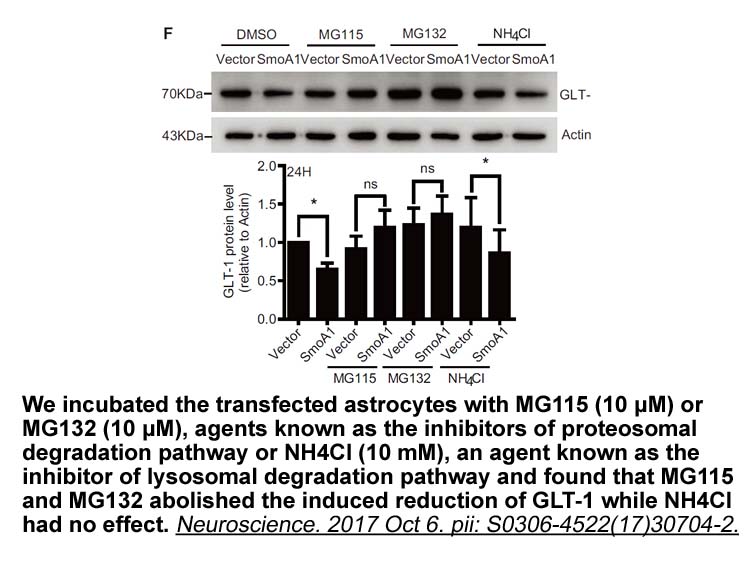
Depletion of PI(4,5)P2, e.g. by knockout of PIPKIγ, also profoundly inhibits SV endocytosis (Di Paolo et al., 2004). Conversely, loss of the PI(4,5)P2-metabolizing PI-phosphatase synaptojanin or its recruitor endophilin stalls SV recycling at the level of clathrin-coated vesicles (Bai et al., 2010,
-
Our data show that oxidative stress high levels of
2022-08-04
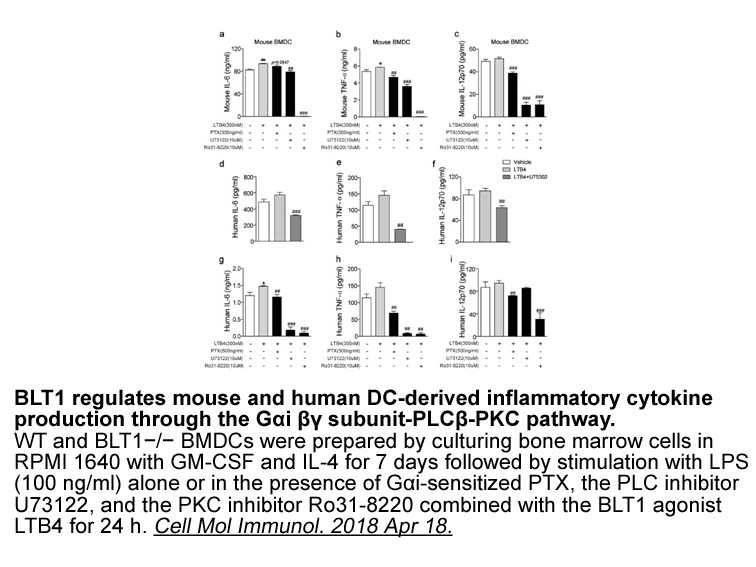
Our data show that oxidative stress (high levels of ROS) suppresses the process of lysosomal exocytosis, which would be predicted to impair the expulsion of toxic compounds from cells. Therefore, we propose that ROS have a biphasic effect on the lysosomal clearance: consistent with their role as a s
-
12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate The effects of C on th
2022-08-04
The effects of C646 on the NF-κB pathway could be explained by the role for p300 that has been described in the regulation of the NF-κB pathway [5]. For instance, acetylations of the p65 NF-κB subunit on lysines 218, 221 and 310 are mediated by the HATs p300 and PCAF [11] and increase transcriptiona
-
In mammalian cells Motins have been identified as a key
2022-08-04
In mammalian cells, Motins have been identified as a key link between F-actin and Hippo pathway regulation, as knockdown of all three Motins increased Yap activity even in the presence of cytoskeletal disruption [105]. Motins can physically associate with F-actin but this association is blocked by p
-
Most hexokinases are widely expressed but distinct hexokinas
2022-08-04
Most hexokinases are widely expressed but distinct hexokinases predominate specific tissues (Katzen and Schimke, 1965, Rogers et al., 1975). Hexokinase I is found in all mammalian tissues, but is most abundant in the NESS 0327 and kidney (griffin et al., 1992). Hexokinase II is the primary hexokina
-
Subcellular domains where Rac is active show limited Rho act
2022-08-04
Subcellular domains where Rac is active show limited Rho activity and vice versa (Fig. 4). This distinctive patterning in Rho activity is achieved via the downstream Rac effector Par6, an important part of the so-called Par polarity complex. In primary epithelium, the cytoskeleton and associated Rho
-
br Acknowledgement br Introduction Malignant melanoma
2022-08-04
Acknowledgement Introduction Malignant melanoma is an aggressive and highly metastatic cancer. The incidence of malignant melanoma is increasing all over the world, and the population of patients with advanced melanoma is growing [1], [2]. Malignant melanoma is often resistant to conventional
-
Here we demonstrate an anti inflammatory and
2022-08-04
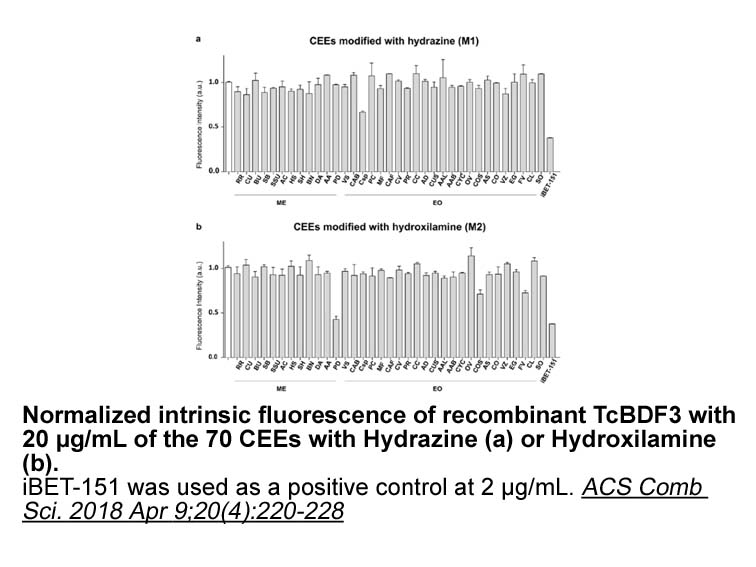
Here we demonstrate an anti-inflammatory and anticancer function for Gpr109a in colon. Gpr109a signaling imposed anti-inflammatory properties in colonic antigen-presenting cells, which in turn induced differentiation of Treg Captopril and IL-10-producing T cells. Gpr109a was also required for the ex
-
br Signaling pathways activated by pulsatile GnRH In the pit
2022-08-04
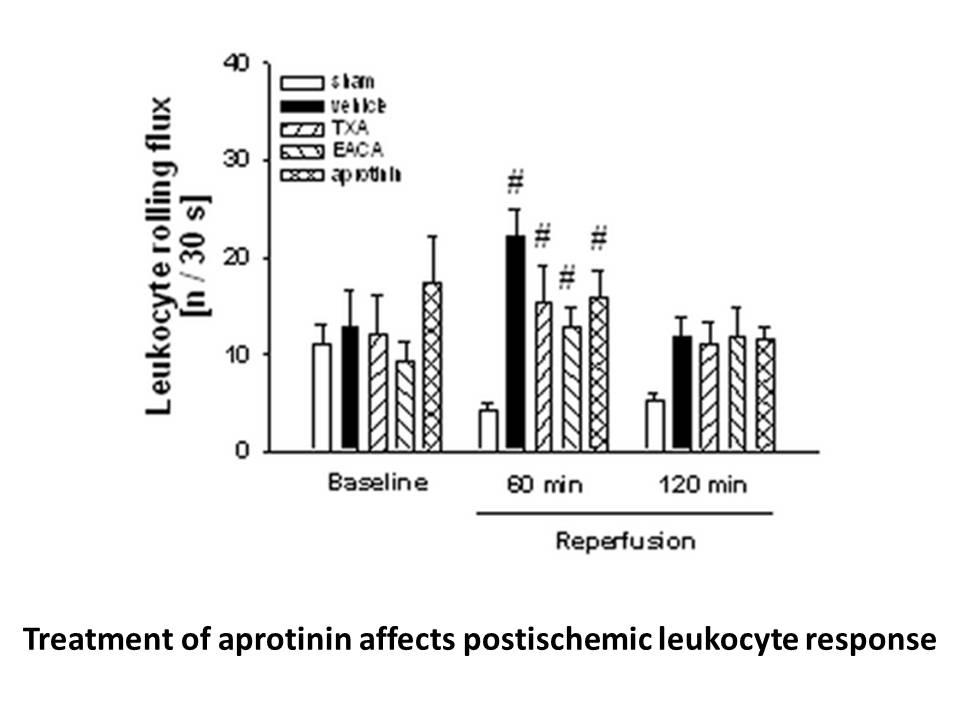
Signaling pathways activated by pulsatile GnRH In the pituitary, GnRH acts by binding to the G protein-coupled GnRHR on the cell surface of the gonadotrope, inducing interaction of the receptor with heterotrimeric G proteins and catalyzing GTP-GDP exchange on the G protein α subunit (Lambert, 200
-
br Inclusion exclusion criteria br Quality assessment
2022-08-03
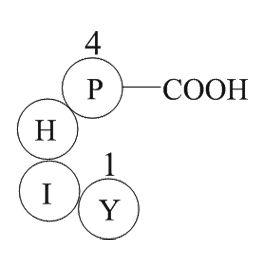
Inclusion/exclusion criteria Quality assessment All studies included in the qualitative synthesis were evaluated using the Quality Assessment Tool for Quantitative Studies (QATQS), which allows to determine their methodological quality. QATQS assesses 8 sections: selection bias, study design,
-
It is notable that pharmacological or genetic
2022-08-03
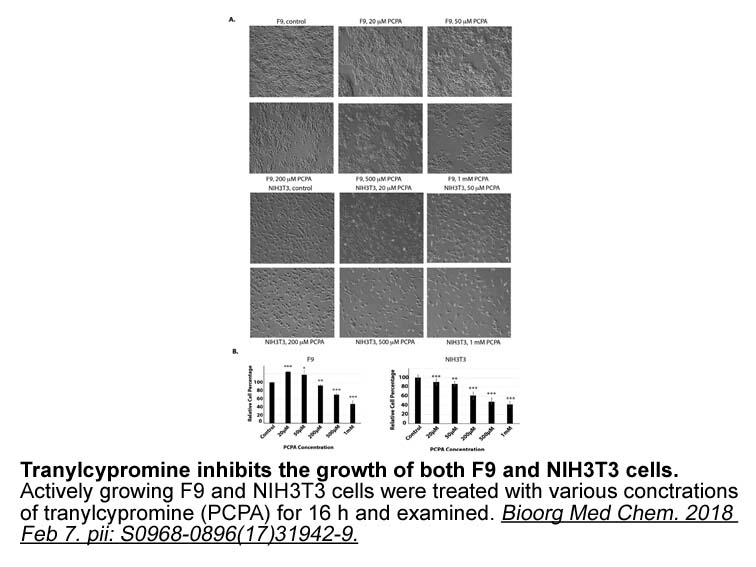
It is notable that pharmacological or genetic inhibition of GCGR signaling results in the engagement of a number of compensatory mechanisms that potentially impact glucose control. These include alpha-cell hyperplasia [2], [11], [12], [13] and increased beta-cell proliferation under low insulin cond
-
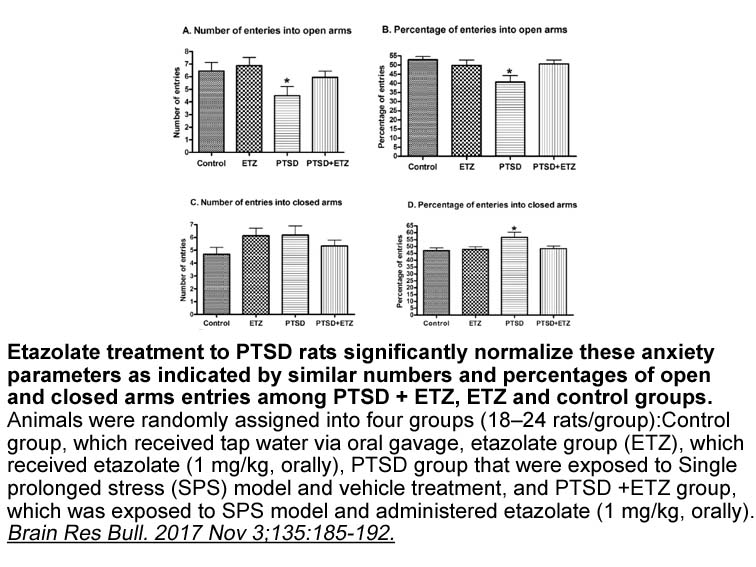
A single ICV injection of GALP stimulated food
2022-08-03
A single ICV injection of GALP stimulated food intake in goldfish at 1h post-administration. This result is similar to that observed in rats, where ICV injection of GALP exerted an acute orexigenic effect [14], [15], [16]. Simultaneously, our findings counter the results found in mice, where central
-
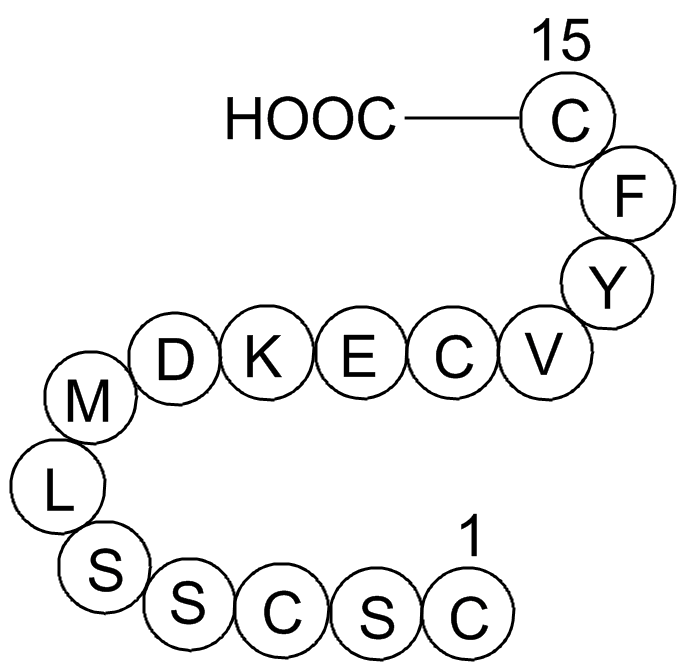
To date three GAL subtype
2022-08-03
To date, three GAL subtype receptors have been cloned and characterized, GALR1, GALR2 and GALR3. However, it is unknown which one(s) of the three subtype receptors in so much is most effective to regulate insulin resistance in diabetic rats as yet. Recent studies fromanimalmodels of diabetes and obe
-
Binding of FGFs to FGFRs leads
2022-08-03
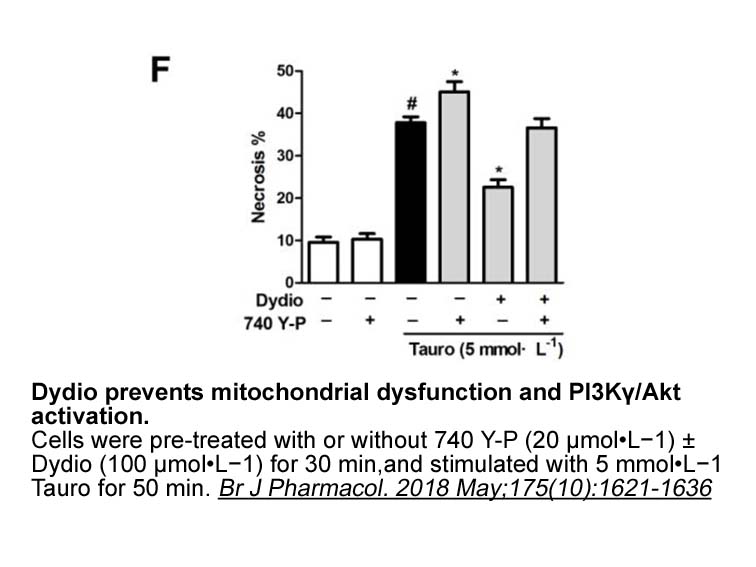
Binding of FGFs to FGFRs leads to receptor dimerization, resulting in the transphosphorylation of a tyrosine in the activation loop of the kinase domain. Subsequently, the activated FGFRs phosphorylate their intracellular receptor substrates, particularly FGFR substrate 2 (FRS2) and phospholipase Cγ
15943 records 384/1063 page Previous Next First page 上5页 381382383384385 下5页 Last page